Introduction to Human Pathology
Human pathology is the study of diseases and how they affect the human body. It is a branch of medical science that deals with the diagnosis and treatment of illnesses. Pathologists are medical professionals who study diseases and disorders to help diagnose and treat them. They use laboratory tests, imaging techniques, and other methods to identify the cause of a disease and develop a treatment plan.
There are many different types of diseases that can affect the human body, including infectious diseases, genetic diseases, and autoimmune disorders. Infectious diseases are caused by viruses, bacteria, fungi, or parasites. These diseases can be treated with antibiotics, antiviral medications, or other drugs. Genetic diseases are caused by inherited mutations in genes. These can be treated with gene therapy, which involves replacing or repairing the faulty gene.
Autoimmune disorders occur when the immune system attacks the body’s own tissues. These diseases can be difficult to treat, but there are medications available that can help control the symptoms. Cancer is another type of disease that can affect the human body. It occurs when cells in the body grow and divide uncontrollably, forming a tumor. Cancer can be treated with surgery, chemotherapy, radiation therapy, or a combination of these treatments.
Pathologists play an important role in the diagnosis and treatment of these diseases. They examine samples of tissue or body fluids to look for signs of disease. They also use imaging techniques, such as X-rays and MRIs, to get a better look at the body’s internal structures. Once they have made a diagnosis, they work with other healthcare professionals to develop a treatment plan.
In addition to diagnosing disease, pathologists also study the causes of diseases. They may investigate outbreaks of infectious diseases to identify the source of the outbreak and prevent it from spreading. They may also study the effects of environmental toxins on the body, or the role of genetics in the development of certain diseases.
Overall, human pathology is a critical field in medicine. It helps us understand the nature of diseases and how they affect the human body. By studying diseases at the molecular and cellular level, pathologists are able to develop new treatments and improve the health of patients. If you are interested in pursuing a career in healthcare, human pathology is a fascinating and rewarding field to consider.
Hematology:
Hematology is a branch of medical science that deals with the study of blood and blood-forming tissues. It is concerned with the diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of diseases related to the blood cells, bone marrow, and lymphatic system. Hematologists are medical professionals who specialize in the diagnosis and treatment of blood disorders. They are trained to analyze blood samples and use various laboratory techniques to determine the underlying cause of blood-related diseases.
The study of hematology encompasses a wide range of conditions, including anemia, leukemia, lymphoma, and multiple myeloma. Anemia is a condition in which the body does not have enough red blood cells to carry oxygen to the tissues. Leukemia is a type of cancer that affects the bone marrow and blood cells. Lymphoma is a cancer that affects the lymphatic system, which is responsible for fighting infections in the body. Multiple myeloma is a type of cancer that affects the plasma cells in the bone marrow.
Hematologists use a variety of techniques to diagnose and treat these conditions. They may use blood tests to examine the number and type of blood cells in the body. They may also use bone marrow biopsies to examine the bone marrow and determine if it is producing abnormal cells. In addition, they may use imaging tests, such as CT scans or MRIs, to look for abnormalities in the lymphatic system.
Once a diagnosis has been made, hematology treatments may include blood transfusions, chemotherapy, radiation therapy, or bone marrow transplants. Blood transfusions involve the transfer of blood or blood products from one person to another. Chemotherapy is a treatment that involves the use of drugs to kill cancer cells. Radiation therapy is a treatment that involves the use of high-energy radiation to kill cancer cells. Bone marrow transplants involve the transfer of healthy bone marrow cells to replace damaged or diseased bone marrow.
In addition to treating blood disorders, hematologists also play an important role in the prevention of blood-related diseases. They may work with patients to identify risk factors for developing blood disorders and recommend lifestyle changes or medications to reduce these risks. For example, they may recommend that patients with a family history of blood disorders undergo genetic testing to determine if they are at increased risk.
Overall, hematology is an essential part of modern medicine. Hematologists play a critical role in the diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of blood-related diseases. Through their research and clinical work, they continue to develop new techniques and treatments that improve the quality of life for patients with blood disorders.
Body Fluids
Body fluids are essential to the human body for the maintenance of life. They include blood, urine, cerebrospinal fluid, saliva, sweat, and other fluids secreted by the body. These fluids play important roles in delivering nutrients and oxygen to cells, removing waste products from the body, and maintaining the balance of electrolytes and other substances in the body.
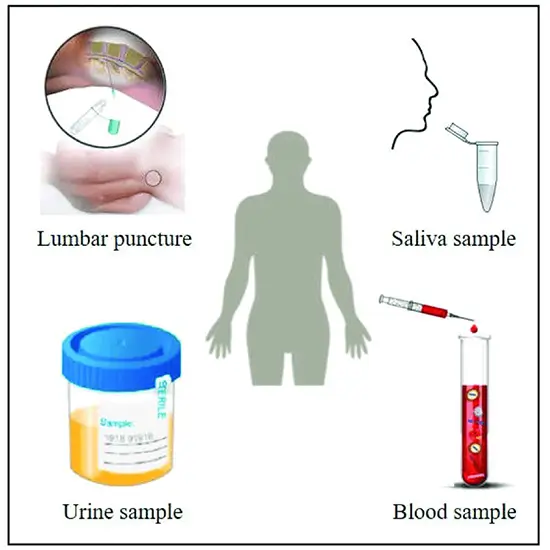
Blood is the most well-known and vital body fluid in the human body. It circulates oxygen, nutrients, and other essential substances throughout the body, while also carrying away waste products such as carbon dioxide. It also contains immune cells that help fight against infections and diseases. Blood is composed of plasma, red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets.
Urine is another important body fluid that is produced by the kidneys. It contains waste products such as urea, creatinine, and excess salts and water. Urine is normally sterile but can become contaminated with bacteria if the urinary system is infected. Urine analysis is a common diagnostic tool used to detect a wide range of conditions, including urinary tract infections, kidney disorders, and diabetes.
Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) is a clear liquid that surrounds the brain and spinal cord. It is produced in the brain’s ventricles and helps protect the brain and spinal cord from injury. CSF also helps remove waste products from the brain and spinal cord and delivers nutrients to these structures. Analysis of CSF can be used to diagnose a range of conditions, including meningitis, encephalitis, and some types of tumors.
Saliva is a fluid that is produced by the salivary glands in the mouth. It helps moisten food and contains enzymes that begin the digestion process. Saliva also contains antibodies that help protect against infections and diseases.
Sweat is a body fluid that is produced by sweat glands in the skin. It contains water, salt, and other electrolytes, and helps regulate body temperature by evaporating from the skin’s surface. Sweat can also contain traces of other substances, such as drugs and alcohol, that can be used for diagnostic purposes.
Overall, body fluids are essential to the proper functioning of the human body. They play important roles in delivering nutrients and oxygen to cells, removing waste products, and helping to protect against infections and diseases. Analysis of body fluids is a common diagnostic tool used by healthcare professionals to diagnose a wide range of conditions and diseases. Understanding the properties and functions of body fluids is a critical part of modern medicine.
What are main 4 types of pathology?
There are several types of pathology, but here are four common ones:
Anatomic Pathology: This type of pathology involves the examination of tissue samples from the body to diagnose diseases.
Clinical Pathology: This type of pathology focuses on the analysis of bodily fluids and tissues to diagnose diseases and monitor their progression.
Molecular Pathology: This type of pathology involves the study of DNA, RNA, and proteins to diagnose and treat diseases at the molecular level.
Forensic Pathology: This type of pathology involves the investigation of sudden, unexpected, or suspicious deaths.
| Read on Human Physiology | Read on Human Anatomy |


Pingback: COMMUNITY MEDICINE -
Pingback: FUNDAMENTALS OF AYURVEDA -
Pingback: Fasting nutrition dietetics -
Pingback: The Role of Physiotherapy : Improving Physical Function and Enhancing Quality of Life -
Pingback: YOGA THERAPY: The Healing Power of Yoga -
Pingback: Acupressure - Healing power of acupressure -
Pingback: Common diseases and remedies -
Pingback: common mental disorders -
Pingback: Acupuncture: An Ancient Therapy for Modern Times -